The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has finally developed a cheap and efficient recyclable flow battery that can store intermittent energy sources such as solar energy and wind energy, which is 10 times more powerful than most lithium batteries. So what exactly is a flow battery? It is a recyclable battery that exchanges ions through two liquids with opposite charges (electrolytes) and then directly converts the chemical energy into electrical energy. What is a flow battery? A flow battery is a rechargeable battery in which two liquids with opposite charges (electrolytes) exchange ions and convert chemical energy into electrical energy. There was usually a film that separates the electrolytes so that they do not mix the two liquids when they exchange ions. However, the electrolytes that are often used are not expensive, but they erode the film, which is not cheap, which greatly shortens the life of the battery. So the best way for researchers to achieve their goals is to remove the film directly. In order to keep the two liquids from mixing together, the researchers used a layer flow technique in liquid fluid dynamics to place them in a container. The electrolyte storage is separated from the battery itself. There are two slots for the electrolyte, which means that the size of the battery can be easily controlled. Just change the size of the tank to change the size of the battery. Power generation can range from tens of millions to several megawatts. In addition to the adjustable size, the flow battery has more advantages: “It can be idle for a long time without losing the charge, the response time is fast, and it can be quickly charged and discharged by changing the electrolyte.†Because of this, some people have been in the past few years. This should be used to quickly charge electric vehicles. On the other hand, flow batteries are more complex than regular batteries, each requiring its own pump and sensor system. And the energy density is lower than the average lithium battery. This is the battery of the future Now MIT has made a good balance between performance and cost in the development of flow batteries. The electrolyte used is not expensive, replacing the expensive film and solving the shortcomings of short battery life. The battery prototype at MIT Labs uses a strange phenomenon called laminar flow in fluid hydrodynamics: when the two liquids are kept at a sufficiently low speed and other conditions are met, the two electrolytes do not mix, making the film redundant. The flow battery can generate 0.795 watts per square centimeter of electricity, which is three times that of other thin-film battery design systems and 10 times that of ordinary lithium batteries. Previously, the relevant team also involved thin-film battery systems, but this is the first energy-efficient battery that can be automatically discharged and recharged, and the amplified version of this device is truly influential, it can cost only $100 per kWh. Another advantage is that this technology can be used for storage of renewable energy, because sunlight and wind can be seen as infinite in the short term, so a large amount of clean energy can be stored as a backup. This will be expected to transform solar and wind energy without interruption, making it the best energy choice for our electric vehicles. Hydraulic Power Unit,Hydraulic Power Unit Truck Tailgate,Hydraulic Pump Power Unit,Hyraulic Power Unit For Lifting Huaian Haotian Hydraulic Co.,Ltd , https://www.hahtyy.com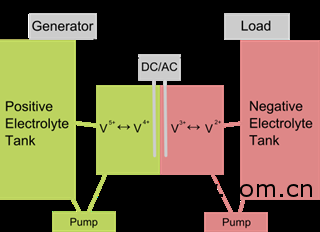
Stay tuned: MIT's new flow battery
Prev Article
Cleverly selecting special automobile spare parts