c) Final shrin temp.: 12 degrees Celsius
Product images:
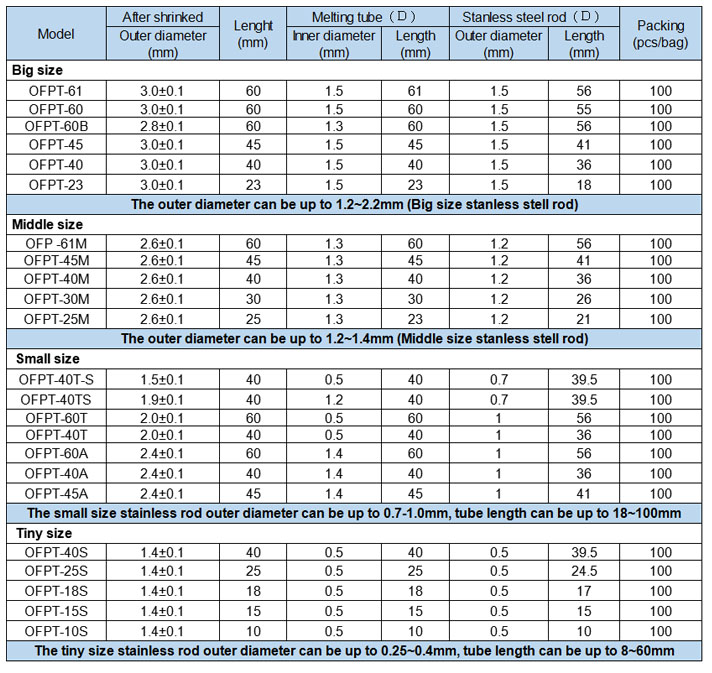
Product dimension:
Fiber Optical Heat Shrinkable Tubing Fiber Heat Shrink Tube,Fiber Optic Heat Shrink Sleeve,Thin Wall Clear Heat Shrink Tubing KEYUACE Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.insulationtubing.com
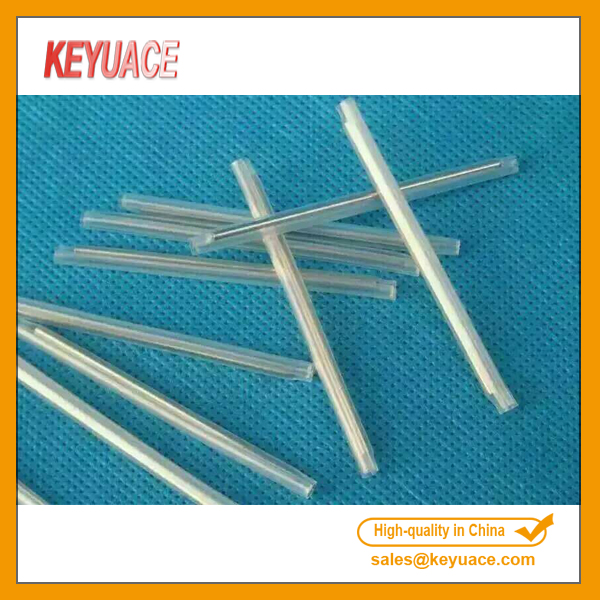
OFPT Single Core Optical Fiber Splice Protection Sleeves
Product Description:
OFPT Single Core Optical Fiber Splice Protection Sleeves is made of transparent heat shrink tube, transparent heat melting tubing and stainless steel rod. Fiber Optical Heat Shrinkable Tubing it applies to coupler, adapter, optical fiber jumper, etc.
Feature & benefit:
a) Do not affect the optical properties of the optical fiber; Protect Splice, improve mechanical strength.
b) Easy to operate, reduce the danger of optical damage during installation.
c) Transparent tube, optical connection status is clear at a glance.
d) Shrinkable, seal structure makes the slice have high temperature resistant and dump-proof properties.
Operating indexes:
a) Working temperature: -45~100 degrees Celsius/-45~135 degrees Celsius
b) Min. Shrink temp.: 80 degrees Celsius


Sorghum lead anode slime wet recovery
First, the test materials and process
High antimony lead anode mud composition Northwest Nonferrous Metal Research Institute used to: Au0.04286%, Ag7.143%, Pb13.75 %, Sb51.36%, Cu2.985%, As1.029%, Bi0.357% . The process flow is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 sorghum lead anode mud wet process
Second, hydrochloric acid leaching copper
The ruthenium in the ruthenium anode is mostly present in Sb 2 O 3 , and a small amount of ruthenium and ruthenium alloy can form a SbCl 3 solution with hydrochloric acid during the leaching process due to the presence of oxygen. The response is:
Sb 2 O 3 +6HCl=2SbCl 3 +3H 2 O
2Sb+1(1/2)O 2 +6HCl=2SbCl 3 +3H 2 O
Copper is mainly composed of metallic copper in the tantalum anode mud. Under the action of oxygen, part of the copper forms Cu 2 (OH) 2 CO 3 , which reacts in hydrochloric acid leaching:
Cu+(1/2) O 2 +2HCl=CuCl 2 +H 2 O
Cu 2 (OH) 2 CO 3 +4HCl=2CuCl 2 +CO 2 ↑+3H 2 O
The CuCl 2 produced by the reaction enters the solution.
Leaching experimental results show that with increasing concentration of hydrochloric acid, copper, antimony also will increase the rate of leaching, the leaching rate of silver and little change, loss of less than 1% of silver, up to 1.26% lead. When the concentration of hydrochloric acid is 4mol/L, the leaching rate of copper and bismuth is more than 90%, and the separation of copper bismuth and silver lead is achieved. The leaching rate of bismuth and copper also increases with the leaching temperature, and when it is greater than 85 °C, the increase is small. Therefore, the leaching conditions are: temperature 85 ° C, hydrochloric acid concentration 4 mol / L, liquid-solid ratio 5:1, time 1.5 h, the leaching results are: 锑 leaching rate of 90.8% ~ 92.6%, copper 93.2% ~ 94.0%, silver Lead is basically retained in the solid phase slag.
3. Chlorinated leaching gold and ammonia leaching silver
The conditions of fixed leaching gold were: hydrochloric acid concentration 1mol/L, temperature 85°C, liquid-solid ratio 5:1, leaching 4h, NaCl concentration 40g/L, and the effect of NaClO3 addition amount was investigated. The experimental results showed that sodium chlorate was added in 10 times. At %, the gold leaching rate was 96.1%, and the silver leaching rate was <1%.
The slag ammonia was immersed in silver after leaching gold with 10% slag sodium dichlorate. The leaching conditions were: ammonia concentration 4 mol/L, temperature 50 ° C, time 1.5 h, liquid-solid ratio 5:1, and silver leaching rate was 92.9%. Analysis of the reason why silver leaching is not high, found that some of the silver in the anode mud is in the form of elemental silver, which must be oxidized to be leached. Therefore, the conditions of the chlorination leaching gold are adjusted, and then the ammonia is immersed in the adjusted slag. In order to oxidize elemental silver, it is considered that the amount of sodium chlorate added during chlorination of gold is increased from 10% to 20%. At this time, ammonia leaching of 20% sodium chlorate leaching residue increased the silver leaching rate to 96.9%.
Considering the leaching rate of immersion silver and leaching gold, the optimum conditions for determining the leaching gold are: the amount of sodium chlorate added is 20% of the slag weight, the leaching temperature is 80-85 ° C, the liquid-solid ratio is 4:1, and the HCl medium concentration is 0.5 mol. /L, leaching time 4h.
4. Gold and silver recycling and lead recycling
When chloride leaching of gold, Au to [AuCl 4] - into the solution, reduction with ferrous sulfate, to obtain powder. The response is:
[AuCl 4 ] - +3Fe 2+ →Au+3Fe 3+ +4Cl -
The standard electrode potential of Fe 3+ /Fe 2+ is lower than [AuCl] - /Au, higher than lead, copper and strontium ions, so it can selectively reduce gold. Because of the liquid ion reduction, the quality of gold is guaranteed. At room temperature, the addition of ferrous ions is 15 times the theoretical requirement of gold, the reduction rate is as good as 99.1%, and the purity is 99.981%. The immersion silver solution requires 1.1 times of hydration of hydrazine, the reduction rate is 99.99% at room temperature to 50 ° C, the liquid silver content after reduction of silver is 0.56 μg / mL, and the purity of silver powder is 99.972%.
The crucible was replaced by iron filings from the dip liquid, and the excess iron scrap was replaced at 70-80 ° C for 1.5 h, and the substitution rate was 98.7%. The ratio of iron filings to enthalpy is 1:2. Lead is produced in concentrate, with a lead content of 50% to 59%. There is no waste residue output during the whole process.
Prev Article
Granite introduction