Mechanical Plate,Plastic Injection Parts,Drill Press Fixture Plate,Threaded Fixture Plate Kun Shan Qi Dian Precision Mold Co., LTD , https://www.qidian-mold.com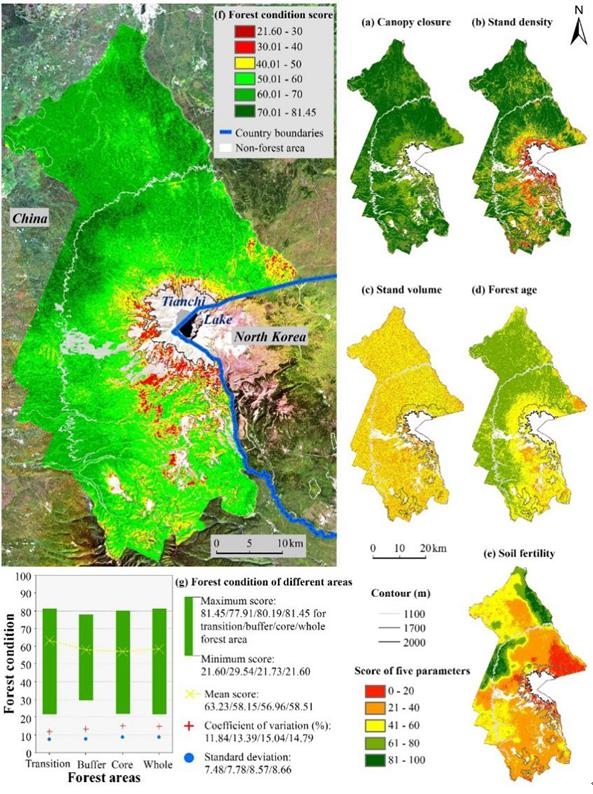
Progress in Remote Sensing Evaluation of Forest Health Status in Northeast China
[ Instrument R & D of Instrument Network ] The forest ecosystem is the main body of the terrestrial biosphere and plays an irreplaceable role in ensuring the functions of terrestrial ecosystems and mitigating global warming. Forest health is an important basis for ecological assessment and scientific management, which is reflected in ecosystem stability, resilience, carbon storage capacity, and wood productivity. The emergence of multi-source remote sensing data and the extensive application of machine learning algorithms have made breakthrough results in remote sensing inversion of important ecological parameters of forest vegetation with multi-scale and high accuracy, and also provided an effective way for remote sensing evaluation of forest ecosystem health status.
Since the launch of the first man-made earth resource satellite in the late 1960s, space remote sensing technology has made great strides, playing an increasingly important role in the economic, political, and military fields of various countries around the world, and the ground resolution of remote sensing satellites It is getting higher and higher, the amount of information obtained is getting bigger and bigger, and the application range is getting wider and wider. At present, multi-platform, multi-temporal, multi-spectral and multi-resolution remote sensing image data is rapidly coming in an alarming amount. This is what we call multi-source remote sensing.
Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve joined the UNESCO International “Man and Biosphere†network of protected areas in 1980. The large existing virgin forests are regarded as the most typical natural complexes of animal and plant species in Eurasia. Under the combined effect of climate change and human factors, what is the health status of the forest ecosystem in the reserve? Are there significant spatial differences at the regional scale? The above questions need to be answered urgently. Based on multi-source remote sensing data and machine learning algorithms, remote sensing estimation and comprehensive assessment of health status of important forest ecological parameters in protected areas are realized. For understanding the spatial variability of forest ecosystem structure and function, supporting the sustainable management and protection of forests in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve The safety of regional ecosystems has important scientific value and practical significance.
Compared with single-source remote sensing image data, the information provided by multi-source remote sensing image data is redundant, complementary and cooperative. The redundancy of multi-source remote sensing image data indicates that they have the same representation, description or interpretation of the environment or target; complementarity means that the information comes from different degrees of freedom and is independent of each other; cooperative information is when different sensors observe and process information Dependence on other information.
Researchers of the Geographical Landscape Remote Sensing Discipline Group of the Northeast Institute of Geography and Agricultural Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences selected important ecological parameters such as forest age, canopy density, standing tree density, stock volume and soil fertility as evaluation indicators, based on ALOS-2L band radar data and Sentinel Satellite C-band radar and visible light images, ALOSDSM data and a large number of field survey data, carried out remote sensing inversion research on forest structure and function parameters of Changbai Mountain, and applied it to forest health assessment. The research system analyzes the relationship between remote sensing factors and various parameters, and through statistical regression, random forest, random forest kriging and other spatial modeling methods, inversion obtained Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve forest age, canopy density, standing tree density, Spatial distribution of accumulation and soil fertility parameters; on this basis, using the principal component analysis method to determine the weight of each parameter, construct the Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve forest health assessment model, and the uncertainty analysis of the assessment results.
The spatial registration of images is a prerequisite for the fusion of remote sensing image data. For the spatial registration of two images, one of them is generally referred to as a reference image, and the other image is corrected based on it. Space registration can generally be divided into the following steps:
(1) Feature selection: On the two images to be registered, select obvious features such as borders, line intersections, and area contours.
(2) Feature matching: A certain registration algorithm is used to find the corresponding obvious object points on the two images as the control points.
(3) Spatial transformation: According to the control points, the mapping relationship between the images is established
(4) Interpolation: Resample non-reference images according to the mapping relationship to obtain images that are registered with the reference image. The accuracy of spatial registration is generally required to be within 1 to 2 pixels. The most critical and difficult step in spatial registration is to find the corresponding obvious object points as control points through feature matching.
The study found that the biophysical variables of the Sentinel-2 image have a significant generalized linear relationship with the forest canopy density and standing tree density. The topographic factors of L-band interferometric radar and the spectral index of visible light contribute greatly to the inversion of forest age and soil fertility. Among the radar backscatter characteristics, HV polarization and VV polarization are more sensitive to the spatial variability information of parameters such as stock volume, forest age and soil fertility. The high-precision remote sensing inversion results show that the forest canopy density, standing tree density and forest age of Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve all show the law of differentiation that decreases along the elevation gradient. According to the results of the spatial assessment of forest health status, the spatial difference of forest health status in Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve is mainly affected by soil fertility and accumulation; the forest quality status in different functional areas is not significantly different, but the forest quality status in the core area varies The coefficient is the highest. The study proposed a technical route and method for forest health assessment based on multi-source remote sensing data. The research results can provide an important reference for scientific and effective forest management and protection measures in protected areas.
Source: Northeast Institute of Geography and Agricultural Ecology, Encyclopedia